Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Problem Type: Monotonic Stack
Related Problems:
Problem
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
1 <= heights.length <= 10⁵0 <= heights[i] <= 10⁴
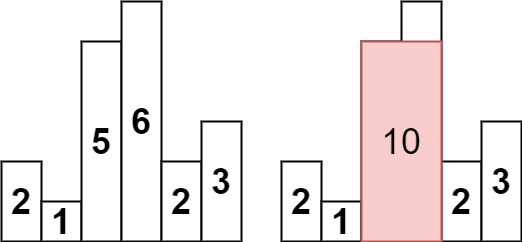
Input: heights = [2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3]
Output: 10
Explanation: The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area of 10 units.
Input: heights = [2, 4]
Output: 4
Explanation: The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area of 4 units.
Solution
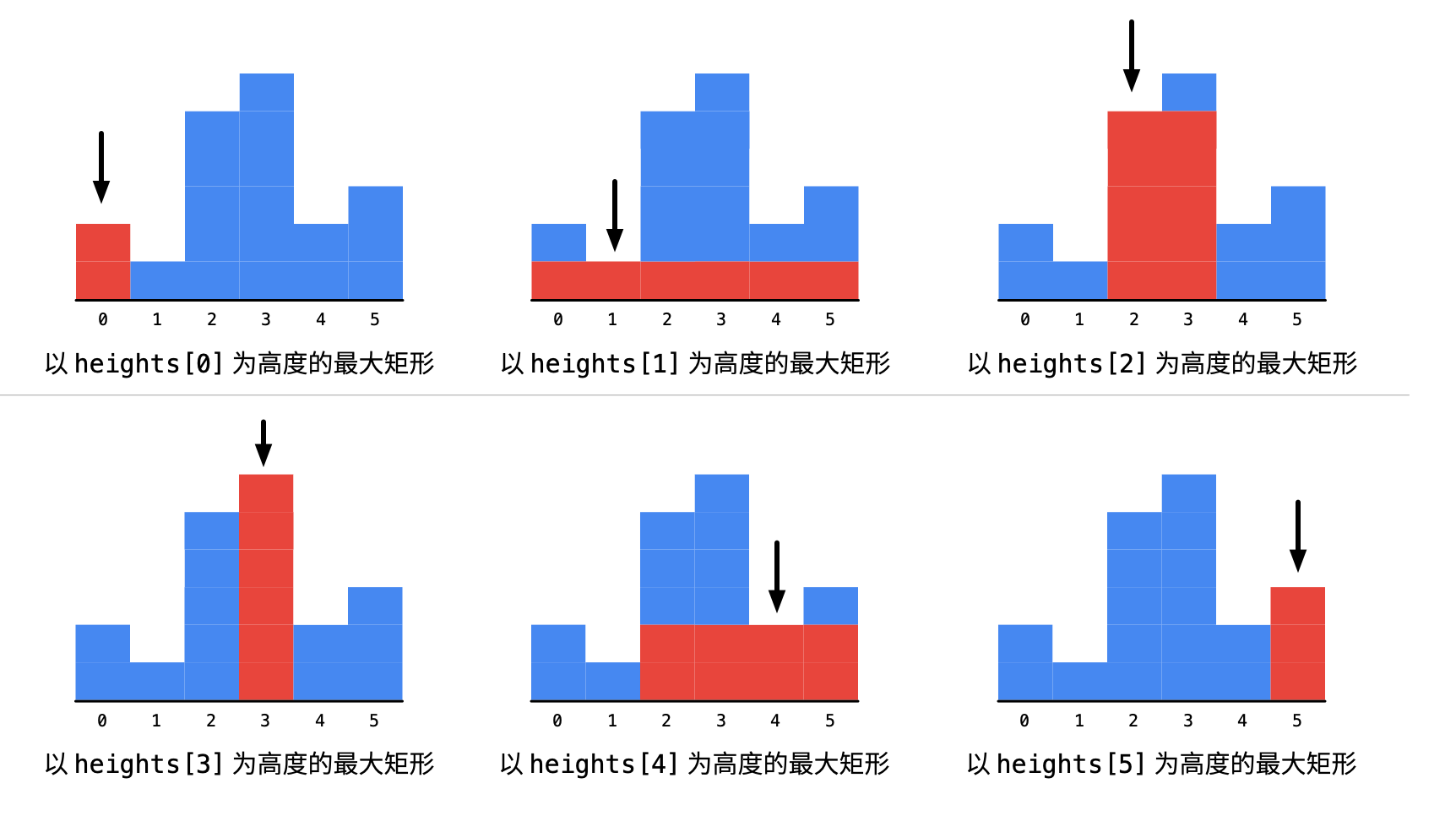
Whether using brute force or monotonic stack, the idea is to take a specific height, for example heights[2] (which is 5) in the first example, then expand in both directions to find the nearest bars that are shorter than it:
- Expand left:
heights[1]is less thanheights[2], meaning to maintain the height ofheights[2], the left boundary must be at index1 - Expand right:
heights[4]is less thanheights[2], meaning to maintain the height ofheights[2], the right boundary must be at index4
Thus, the maximum width maintaining the height heights[2] is 4 - 1 - 1 = 2.
For the brute force approach, we need to iterate through each height, then use it as a pivot and expand left and right to find the left and right boundaries. However, this results in O(n²) time complexity. Therefore, we can use a space-for-time strategy with a monotonic stack to pre-calculate the left and right boundaries for each bar. See the code comments for the specific implementation.
- JavaScript - Brute Force
- JavaScript - Monotonic Stack
- Rust
/**
* @param {number[]} heights
* @return {number}
*/
var largestRectangleArea = function (heights) {
const n = heights.length
let max = 0
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const height = heights[i]
let left = i
while (left > 0 && heights[left - 1] >= height) {
left--
}
let right = i
while (right < n - 1 && heights[right + 1] >= height) {
right++
}
max = Math.max(max, height * (right - left + 1))
}
return max
}
- Time Complexity:
O(n²) - Space Complexity:
O(1)
/**
* @param {number[]} heights
* @return {number}
*/
var largestRectangleArea = function (heights) {
const n = heights.length
// Find the left boundary (smaller than current element) for each bar
// Default is -1: if all elements to the left are taller,
// we can extend the current height all the way to the left, so the boundary is -1
//
// Note: We use -1 instead of 0 because we're storing indices
const lefts = new Array(n).fill(-1)
// Find the right boundary (smaller than current element) for each bar
// Default is n: if all elements to the right are taller,
// we can extend the current height all the way to the right, so the boundary is n
const rights = new Array(n).fill(n)
const stack = []
// Standard monotonic stack: find the right boundary (smaller element) for each bar
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (stack.length > 0 && heights[stack[stack.length - 1]] > heights[i]) {
rights[stack.pop()] = i
}
stack.push(i)
}
// Standard monotonic stack: find the left boundary (smaller element) for each bar
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (stack.length > 0 && heights[stack[stack.length - 1]] > heights[i]) {
lefts[stack.pop()] = i
}
stack.push(i)
}
let max = 0
// Calculate the maximum area using left/right boundaries and current bar height
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, (rights[i] - lefts[i] - 1) * heights[i])
}
return max
}
- Time Complexity:
O(n) - Space Complexity:
O(n)
use std::cmp;
pub fn largest_rectangle_area(heights: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = heights.len();
let mut left: Vec<isize> = vec![-1; n];
let mut right = vec![n; n];
let mut stack = vec![];
for i in 0..n {
while !stack.is_empty() && heights[stack[stack.len() - 1]] > heights[i] {
right[stack.pop().unwrap()] = i;
}
stack.push(i);
}
for i in (0..n).rev() {
while !stack.is_empty() && heights[stack[stack.len() - 1]] > heights[i] {
left[stack.pop().unwrap()] = i as isize;
}
stack.push(i);
}
let mut max = 0;
for i in 0..n {
let height = heights[i];
let left_idx = left[i];
let right_idx = right[i];
max = cmp::max(max, height * (right_idx as i32 - left_idx as i32 - 1));
}
max
}