填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
题目类型: Tree
题目
给定一个完美二叉树, 其所有叶子节点都在同一层, 每个父节点都有两个子节点. 二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针, 让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点. 如果找不到下一个右侧节点, 则将 next 指针设置为 NULL 初始状态下, 所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL.
进阶:
你只能使用常量级额外空间.
使用递归解题也符合要求, 本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度.
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
输出:
1 -> null
/ \
2 -> 3 -> null
/ \ / \
4 ->5->6-> 7 -> null
题解
- 层序遍历
- 递归
- 最优解法
最朴素的解法, 使用层序遍历, 让每层的元素逐一连接起来, 但这样时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为 O(n)
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, left, right, next) {
* this.val = val === undefined ? null : val;
* this.left = left === undefined ? null : left;
* this.right = right === undefined ? null : right;
* this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {Node}
*/
var connect = function (root) {
if (root !== null) {
const queue = [root]
while (queue.length !== 0) {
const n = queue.length
// 遍历这一层的所有节点
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const curr = queue.shift()
// 连接
if (i < n - 1) {
curr.next = queue[0]
}
// 拓展下一层节点
if (curr.left !== null) {
queue.push(curr.left)
}
if (curr.right !== null) {
queue.push(curr.right)
}
}
}
}
return root
}
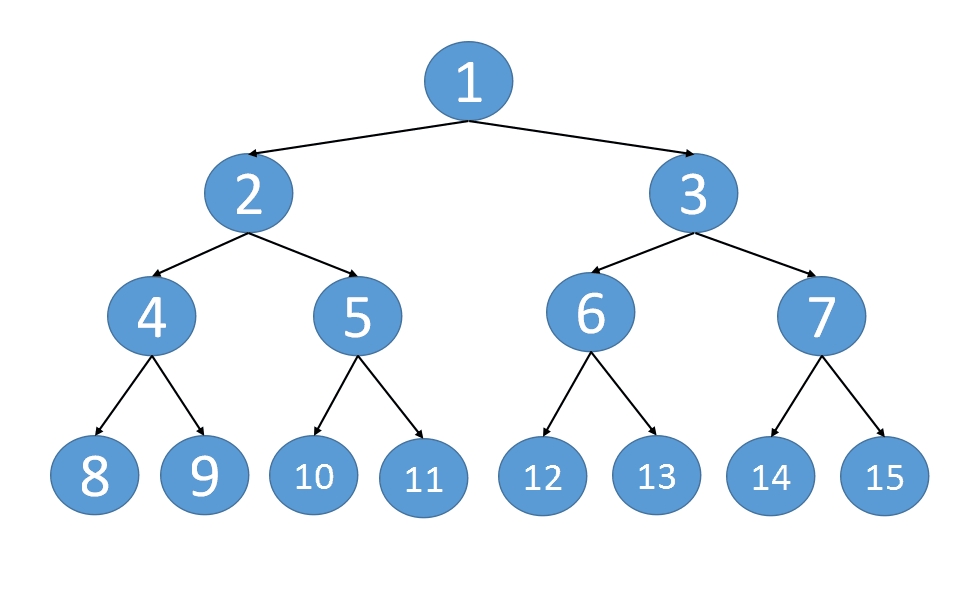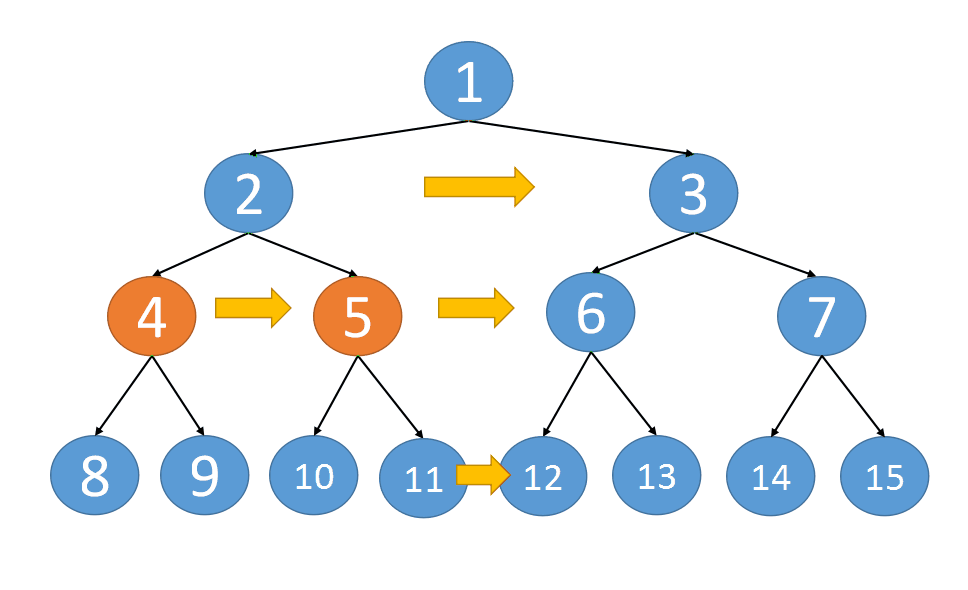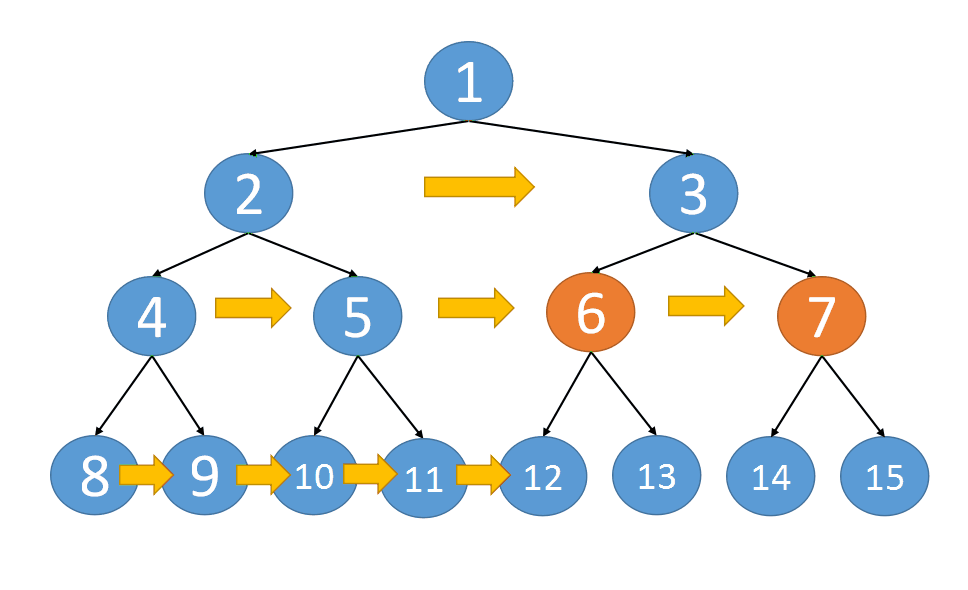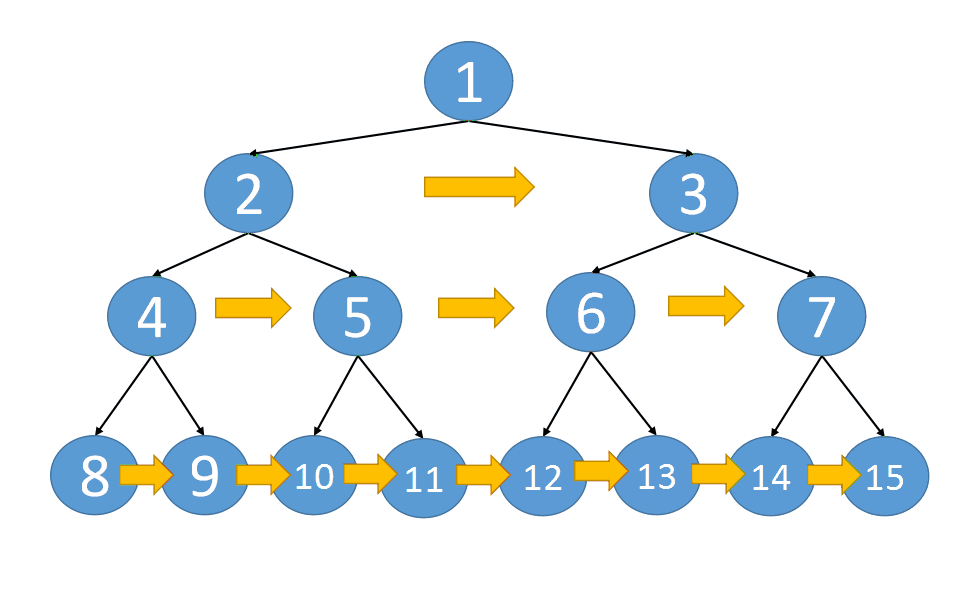
以当前节 root 点为起始, 左右节点不断的深入下面, left 节点不断往右走, right 节点不断往左走, 当这两个节点走到底后, 单个纵深就完成了串联.
递归函数实现如下:
终止条件: 当前节点为空时
函数内: 以当前节点为起始, 完成从上往下的纵深串联, 再递归的调用当前节点 left 和 right
function connect(root) {
dfs(root)
return root
}
function dfs(root) {
if (root == null) {
return
}
let left = root.left
let right = root.right
// 以 root 为起点, 将单个纵深这段串联起来
while (left != null) {
left.next = right
left = left.right
right = right.left
}
// 递归的调用左右节点, 完成同样的纵深串联
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
}
时间复杂度: O(n) 空间复杂度: O(h), h 是树的高度
一棵树中存在两种 next 类型(下面以 node 为 2 那个节点说明):
某个 node 节点的左子节点和左子节点连接, 如 4, 5 两个节点, 它们其实是 2 的子节点, 如果连接的话, 即 node.left.next = node.right
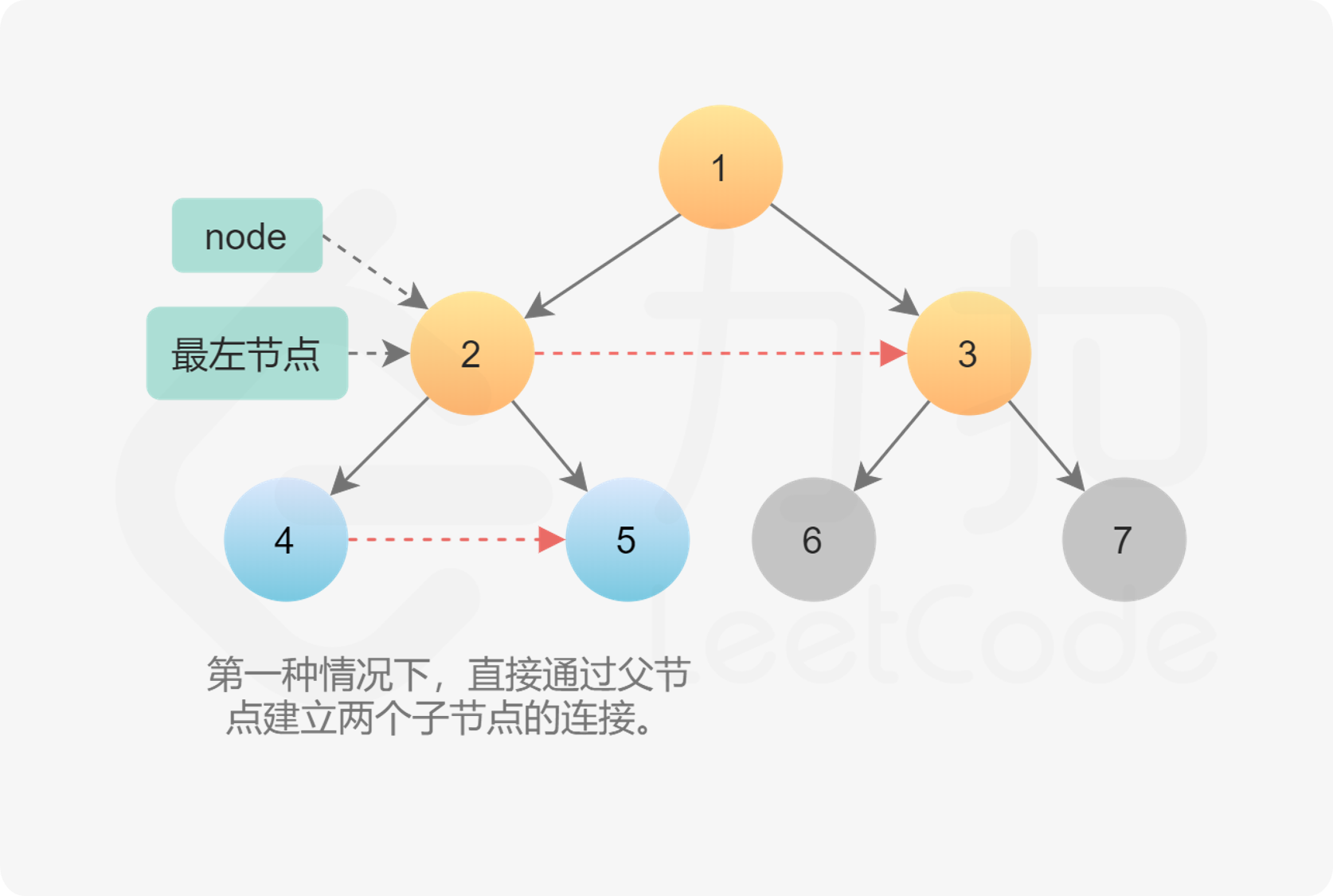
某个 node 节点的右子节点和另一个 node 节点的左子节点连接, 如 5, 6 两个节点. 对于这种情况, 可以和上面结合起来一起看, 5 实际就是 node.right, 而 6 实际就是 node.next.left (注: node.next 是 3), 如果连接的话, 即 node.right.next = node.next.left
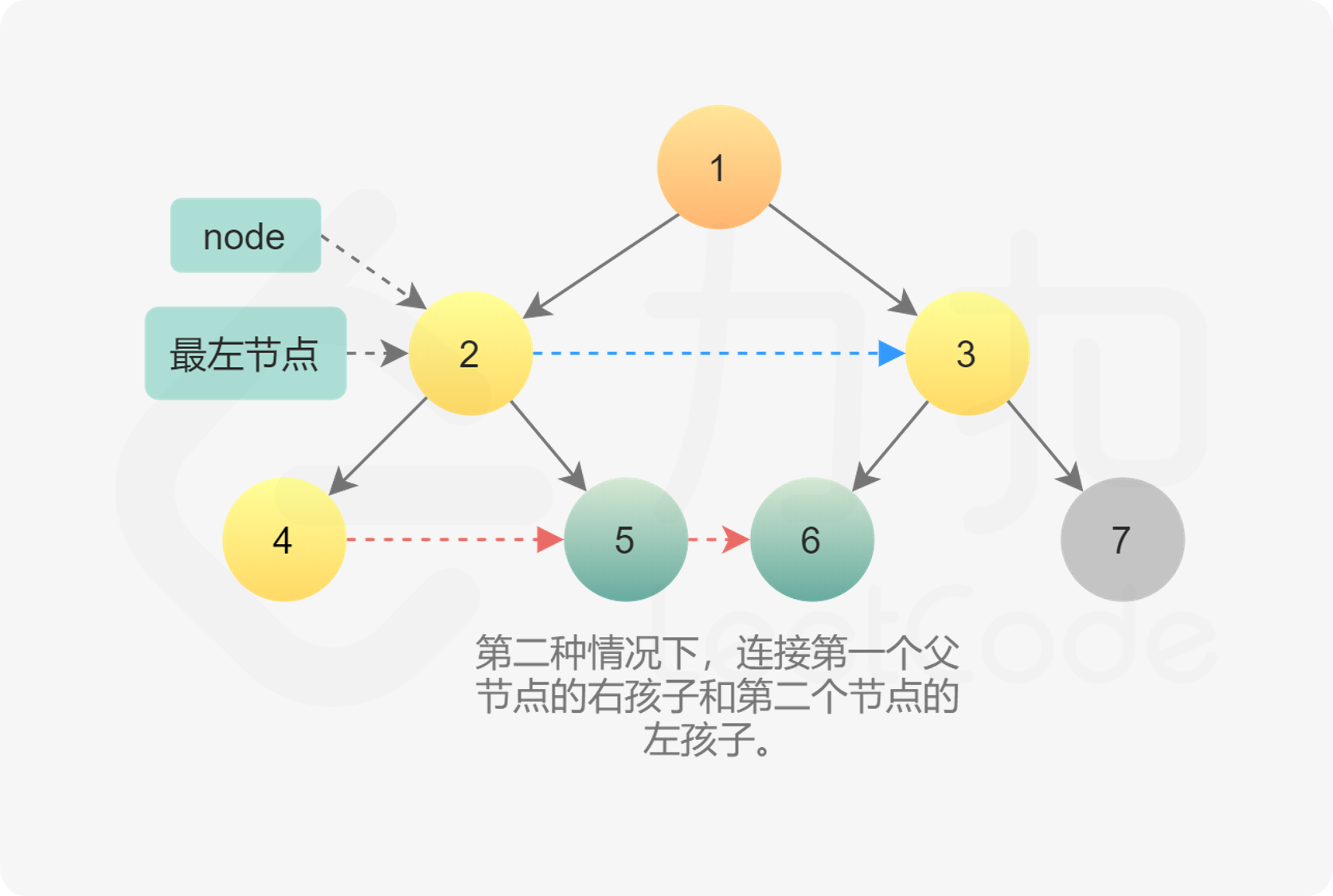
时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为 O(n)
var connect = function (root) {
if (root === null) {
return root
}
// 从根节点开始
let leftmost = root
while (leftmost.left !== null) {
// 遍历这一层节点组织成的链表, 为下一层的节点更新 next 指针
let head = leftmost
while (head !== null) {
// CONNECTION 1: 某个节点的直接左右子节点连接
head.left.next = head.right
// CONNECTION 2: 某个节点的右子节点和另一个节点的左子节点连接
if (head.next !== null) {
head.right.next = head.next.left
}
// 指针向后移动
head = head.next
}
// 去下一层的最左的节点
leftmost = leftmost.left
}
return root
}
时间复杂度: O(N), 每个节点只访问一次
空间复杂度: O(1), 不需要存储额外的节点