扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
题目
给你一个嵌套的整型列表. 请你设计一个迭代器, 使其能够遍历这个整型列表中的所有整数. 列表中的每一项或者为一个整数, 或者是另一个列表. 其中列表的元素也可能是整数或是其他列表.
示例
输入: [[1,1],2,[1,1]]
输出: [1,1,2,1,1]
解释: 通过重复调用 next 直到 hasNext 返回 false, next 返回的元素的顺序应该是: [1,1,2,1,1]
题解
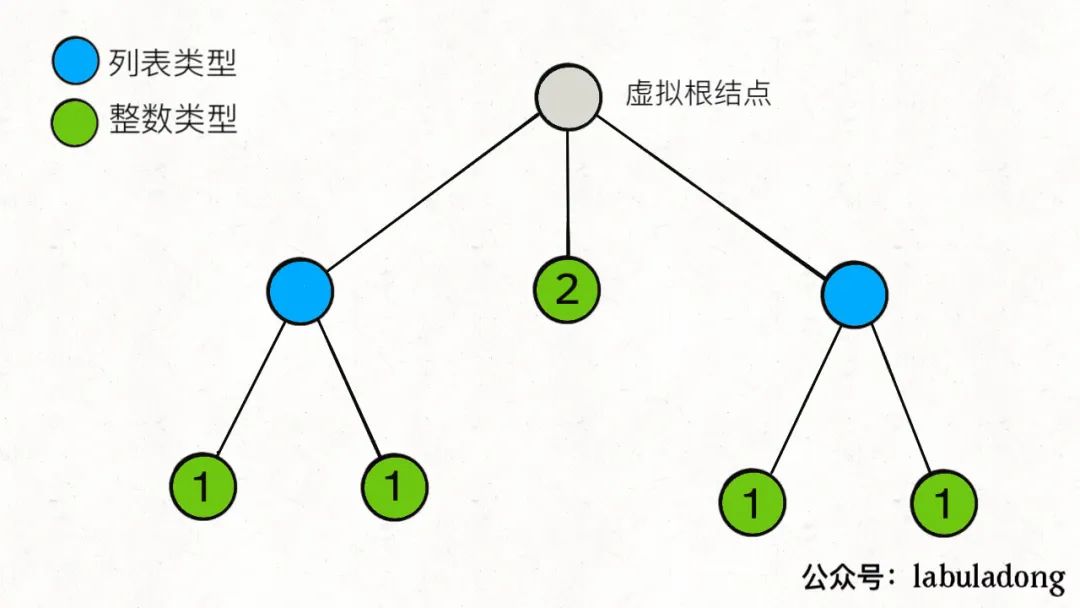
方法一: 递归
由上图可以看出, 嵌套的整型列表是一个多叉树结构, 树上的叶子节点对应一个整数, 非叶节点对应一个列表. 在这棵树上深度优先搜索的顺序就是迭代器遍历的顺序. 我们可以使用递归实现.
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* function NestedInteger() {
*
* Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* @return {boolean}
* this.isInteger = function() {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* @return {integer}
* this.getInteger = function() {
* ...
* };
*
* Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* Return null if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* @return {NestedInteger[]}
* this.getList = function() {
* ...
* };
* };
*/
/**
* @constructor
* @param {NestedInteger[]} nestedList
*/
var NestedIterator = function (nestedList) {
vals = []
const dfs = (nestedList) => {
for (const nest of nestedList) {
if (nest.isInteger()) {
vals.push(nest.getInteger())
} else {
dfs(nest.getList())
}
}
}
dfs(nestedList)
}
/**
* @this NestedIterator
* @returns {boolean}
*/
NestedIterator.prototype.hasNext = function () {
return vals.length > 0
}
/**
* @this NestedIterator
* @returns {integer}
*/
NestedIterator.prototype.next = function () {
const val = vals[0]
vals.shift()
return val
}
/**
* Your NestedIterator will be called like this:
* var i = new NestedIterator(nestedList), a = [];
* while (i.hasNext()) a.push(i.next());
*/
时间复杂度: 初始化为 O(n), next 和 hasNext 方法为 O(1).其中 n 是嵌套的整型列表中的元素个数.
空间复杂度: O(n), 需要一个数组存储嵌套的整型列表中的所有元素.
方法二: 栈
因为递归可以用栈来代替. 具体来说, 用一个栈来维护深度优先搜索时, 从根节点到当前节点路径上的所有节点. 由于非叶节点对应的是一个列表, 我们在栈中存储的是指向列表当前遍历的元素的指针. 每次向下搜索时, 取出列表的当前指针指向的元素并将其入栈, 同时将该指针向后移动一位. 如此反复直到找到一个整数. 循环时若栈顶指针指向了列表末尾, 则将其从栈顶弹出.
var NestedIterator = function (nestedList) {
this.stack = nestedList
}
NestedIterator.prototype.hasNext = function () {
while (this.stack.length !== 0) {
// 如果栈顶是数字, 则返回 true
if (this.stack[0].isInteger()) {
return true
} else {
// 如果栈顶是列表
let cur = this.stack[0].getList()
// 将该列表去掉
this.stack.shift()
// 将该列表中的元素打平, 全都放到栈顶
this.stack.unshift(...cur)
}
}
return false
}
NestedIterator.prototype.next = function () {
return this.stack.shift().getInteger()
}