组合总数
Tips
题目类型: BackTracking
题目
给你一个无重复元素的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target, 找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的所有不同组合, 并以列表形式返回. 你可以按任意顺序返回这些组合.
candidates 中的同一个数字可以无限制重复被选取. 如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同, 则两种组合是不同的.
对于给定的输入, 保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个.
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 302 <= candidates[i] <= 40candidates的所有元素互不相同1 <= target <= 40
示例
输入: candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7], target = 7
输出: [[7], [2, 2, 3]]
输入: candidates = [2, 3, 5], target = 8
输出: [
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[2, 3, 3],
[3, 5],
]
题解
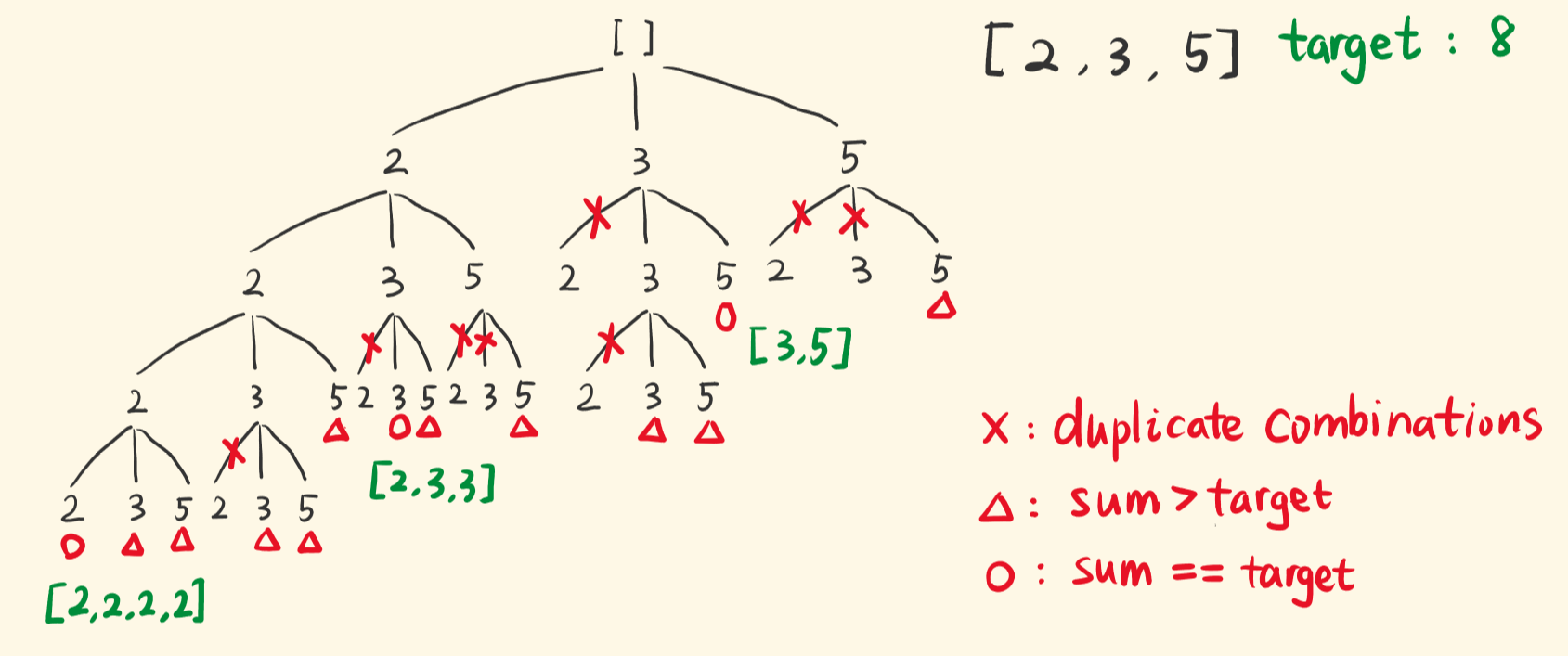
获取数字和为 target 的组合并不难, 即在每次递归探索时将已选列表的值累加, 然后将 sum === target 作为回溯的结束条件即可. 但是这样会导致组合重复, 比如 [2, 5] 和 [5, 2] 都会被输出.
因此我们需要对重复的部分进行剪枝, 只要限制下一次选择的起点, 是基于本次的选择, 这样下一次就不会选到本次选择的同层左边的数. 即通过控制 for 遍历的起点, 去掉会产生重复组合的选项.
- JavaScript
- Rust
/**
* @param {number[]} candidates
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var combinationSum = function (candidates, target) {
const n = candidates.length
const res = []
const dfs = (begin, sum, track) => {
if (target === sum) {
res.push(track)
return
}
for (let i = begin; i < n; i++) {
// 从 begin 开始选择
if (sum < target) {
track.push(candidates[i])
// 基于当前这个数的继续选择, 传 i, 下一次就不会选到 i 左边的数
dfs(i, sum + candidates[i], track.slice())
// 撤销选择, 回到选择 candidates[i] 之前的状态, 继续尝试选同层右边的数
track.pop()
}
}
}
dfs(0, 0, [])
return res
}
pub fn combination_sum(candidates: Vec<i32>, target: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
dfs(0, 0, target, &candidates, &mut vec![], &mut res);
res
}
fn dfs(
begin: usize,
sum: i32,
target: i32,
candidates: &Vec<i32>,
track: &mut Vec<i32>,
res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>,
) {
if sum == target {
res.push(track.to_vec());
return;
}
for i in begin..candidates.len() {
if sum < target {
track.push(candidates[i]);
dfs(i, sum + candidates[i], target, candidates, track, res);
track.pop();
}
}
}