Diagonal Traverse
Problem
Given an m x n matrix mat, return an array of all the elements of the array in a diagonal order.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^41 <= m * n <= 10^4-10^5 <= mat[i][j] <= 10^5
Examples
Example 1:
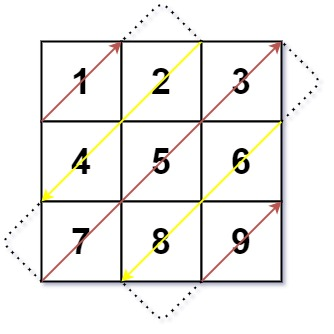
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,4,7,5,3,6,8,9]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Solution
The key to this problem is understanding the diagonal traversal pattern:
- We traverse diagonals in a zig-zag manner
- Odd diagonals (0-indexed) go from bottom-left to top-right (upward)
- Even diagonals go from top-left to bottom-right (downward)
The approach:
- Each diagonal can be identified by the sum of its row and column indices (
i + j) - For diagonal
d, when going upward, we start from the bottom-left and move to top-right - When going downward, we start from the top-left and move to bottom-right
- We use direction flag to alternate between upward and downward traversals
Alternative approach using simulation:
- Start at position
(0, 0)going upward - When hitting boundaries, change direction and adjust position accordingly
- Continue until all elements are visited
- JavaScript
- Rust
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDiagonalOrder = function (mat) {
const m = mat.length
const n = mat[0].length
const result = []
let row = 0
let col = 0
let direction = 1 // 1 for up, -1 for down
for (let i = 0; i < m * n; i++) {
result.push(mat[row][col])
if (direction === 1) {
// Going up
if (col === n - 1) {
// Hit right boundary
row++
direction = -1
} else if (row === 0) {
// Hit top boundary
col++
direction = -1
} else {
// Continue going up
row--
col++
}
} else {
// Going down
if (row === m - 1) {
// Hit bottom boundary
col++
direction = 1
} else if (col === 0) {
// Hit left boundary
row++
direction = 1
} else {
// Continue going down
row++
col--
}
}
}
return result
}
pub fn find_diagonal_order(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
if mat.is_empty() || mat[0].is_empty() {
return vec![];
}
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut result = Vec::with_capacity(m * n);
let mut row = 0;
let mut col = 0;
let mut direction = 1; // 1 for up, -1 for down
for _ in 0..m * n {
result.push(mat[row][col]);
if direction == 1 {
// Going up
if col == n - 1 {
// Hit right boundary
row += 1;
direction = -1;
} else if row == 0 {
// Hit top boundary
col += 1;
direction = -1;
} else {
// Continue going up
row -= 1;
col += 1;
}
} else {
// Going down
if row == m - 1 {
// Hit bottom boundary
col += 1;
direction = 1;
} else if col == 0 {
// Hit left boundary
row += 1;
direction = 1;
} else {
// Continue going down
row += 1;
col -= 1;
}
}
}
result
}
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
O(m * n)- We visit each element in the matrix exactly once. - Space Complexity:
O(1)- Excluding the output array, we only use constant extra space for variables (row, col, direction).